Annuities
Annuities are financial products which entitle the purchaser i.e. annuitant to receive periodic payments during his retirement period (also called distribution period) in exchange of premium(s) paid by the annuitant during the accumulation period. They are a valuable tool in retirement planning because they offer a base income generally for the remaining life of the annuitants.
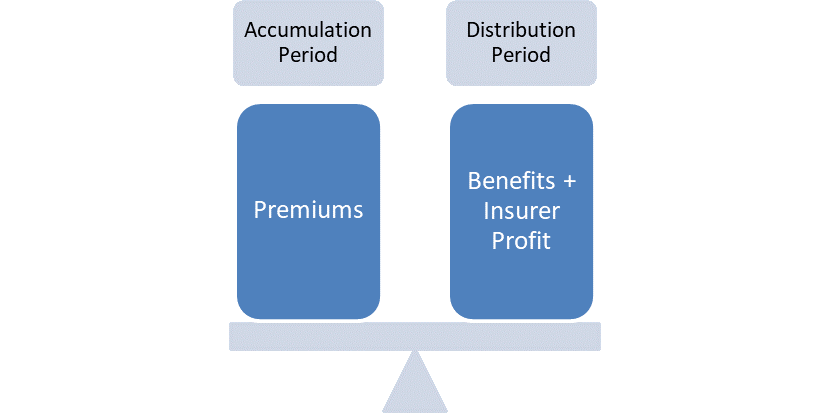
Think of an annuity as a lever, the left-hand side representing the premiums you pay over the accumulation period, the retirement date being the fulcrum and the right-hand side representing the benefits you receive from the insurance company. The insurance company prices the annuity such that the premiums collected are enough to pay off the promised benefits over the life of the surviving annuitants plus the insurer’s profit.
Types
There are four basis ways in which annuities and their classification can differ:
- The way in which the premiums accumulate i.e. whether they are one off payments or a series of payments,
- The time at which the benefits payout starts i.e. whether immediate or deferred.
- The duration and scope of the benefits payments i.e. whether they continue after the death of the annuitant or not; and
- The way the periodic benefits are worked out, i.e. real vs nominal and fixed vs variable.
Single premium annuity vs installment premium annuity
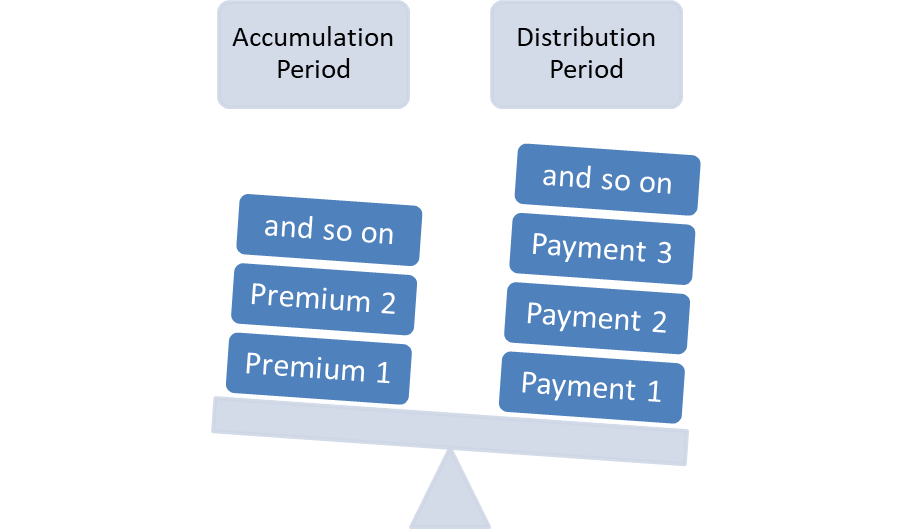
In a single premium annuity, a one large payment is required to be made to the insurer to secure the promised benefits are retirement. In a single premium annuity, you are effectively giving up a chunk or whole of your wealth to secure a periodic cash flow stream. The accumulation period is very short in a single premium annuity.
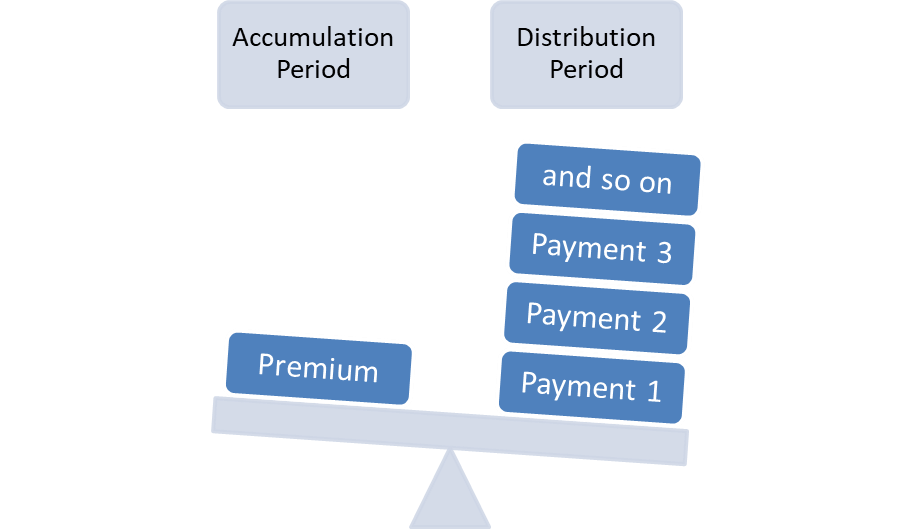
The installment premium annuity is an annuity that requires multiple periodic payments of premiums during the accumulation period.
Immediate annuity vs deferred annuity
In an immediate annuity, the payment of periodic benefits starts right away i.e. within 30 days of the completion of the accumulation period. A single premium immediate annuity is one of the most common annuity structure which involves a single large payment of premium to insurer against benefits payments starting right from the next month. A single premium immediate annuity is appropriate for someone who has
In the deferred annuity, the benefits payout starts after a certain period of time say 2 years of 10 years.
Pure life annuity vs guaranteed minimum annuity vs annuity certain
A pure life annuity pays benefits for the remaining life of the annuitant and there is no minimum or maximum period for which benefits are payable.
A guaranteed minimum annuity is an annuity which specifies that the insurance company will pay a certain minimum level of benefits regardless of when the annuitant dies. It is also called life annuity with refund. There are two types of guaranteed minimum annuities: (a) life annuity, period certain and (b) refund annuity. Life annuity, period certain is an annuity that pays benefits indefinitely to the annuitant but also specifies a period X in which in event of the annuitant’s death, it pays the benefits to the beneficiaries for remaining period X. A refund annuity is an annuity that pays benefits to the annuitant for life but in event of his death, the beneficiaries receive payments until the cost of the annuity is recovered.
An annuity certain is an annuity that pays periodic benefits for a set period of time regardless of when the annuitant dies.
Fixed annuity vs variable annuity
A fixed annuity is an annuity in which the periodic benefits are calculated based on a pre-determined fixed interest rate. A variable annuity on the other hand is an annuity in which the monthly benefits are a function of the actual investment performance of the insurer. If the insurance company performs well, it will pay higher benefits and vice versa.
by Obaidullah Jan, ACA, CFA and last modified on